Product Portfolio
Download as in PDF Format
Spinal / Epidural Hematomas
Epidural or spinal hematomas may occur in patients who are anticoagulated with low molecular weight heparins (LMWH) or heparinoids and are receiving neuraxial anesthesia or undergoing spinal puncture. These hematomas may result in long-term or permanent paralysis. Consider these risks when scheduling patients for spinal procedures. Factors that can increase the risk of developing epidural or spinal hematomas in these patients include:
• Use of indwelling epidural catheters
• Concomitant use of other drugs that affect hemostasis, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), platelet inhibitors, other anticoagulants.
• A history of traumatic or repeated epidural or spinal punctures
• A history of spinal deformity or spinal surgery
Monitor patients frequently for signs and symptoms of neurological impairment. If neurological compromise is noted, urgent treatment is necessary. Consider the benefits and risks before neuraxial intervention in patients anticoagulated or to be anticoagulated for thromboprophylaxis.
Description
Venoxtaj is a sterile aqueous solution containing enoxaparin sodium, a low molecular weight heparin. The pH of the injection is 5.5 to 7.5.
Enoxaparin sodium is obtained by alkaline depolymerization of heparin benzyl ester derived from porcineintestinal mucosa. Its structure is characterized by a 2-O-sulfo-4-enepyranosuronic acid group at the non-reducing end and a 2-N,6-O-disulfo-D-glucosamine at the reducing end of the chain. About 20% (ranging between 15% and 25%) of the enoxaparin structure contains an 1,6 anhydro derivative on the reducing end of the polysaccharide chain. The drug substance is the sodium salt. The average molecular weight is about 4500 daltons. The molecular weight distribution is:
| Molecular weight | Distribution |
| < 2000 daltons | ≤ 20% |
| 2000 to 8000 daltons | ≥ 68% |
| > 8000 daltons | ≤ 18% |
Structural Formula
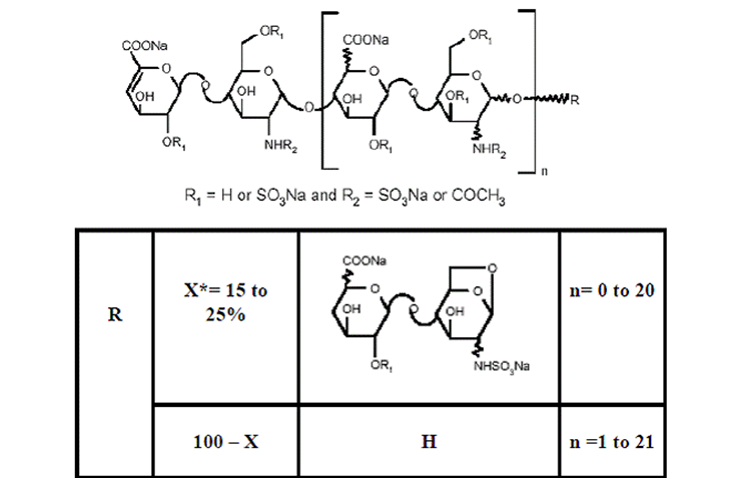
*X = Percent of polysaccharide chain containing 1,6 anhydro derivative on the reducing end.
Venoxtaj 100 mg/mL Concentration contains 10 mg enoxaparin sodium (approximate anti-Factor Xa activity of 1000 IU [with reference to the W.H.O. First International Low Molecular Weight Heparin Reference Standard]) per 0.1 mL Water for Injection.
Venoxtaj 150 mg/mL Concentration contains 15 mg enoxaparin sodium (approximate anti-Factor Xa activity of 1500 IU [with reference to the W.H.O. First International Low Molecular Weight Heparin Reference Standard]) per 0.1 mL Water for Injection.
The Venoxtaj prefilled syringes and graduated prefilled syringes are preservative-free and intended for use only as a single-dose injection. The multiple-dose vial contains 15 mg benzyl alcohol per 1 mL as a preservative
What Are The Possible Side Effects Of Enoxaparin (Venoxtaj)?
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction: hives; itching or burning skin; difficult breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Also seek emergency medical attention if you have symptoms of a spinal blood clot: back pain, numbness or muscle weakness in your lower body, or loss of bladder or bowel control.
Call your doctor at once if you have:
• unusual bleeding, or any bleeding that will not stop;
• easy bruising, purple or red spots under your skin;
• nosebleeds, bleeding gums;
• abnormal vaginal bleeding, blood in your urine or stools;
• coughing up blood or vomit that looks
Indications
Prophylaxis of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Venoxtaj® is indicated for the prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which may lead to pulmonary embolism (PE):
• in patients undergoing abdominal surgery who are at risk for thromboembolic complications
• in patients undergoing hip replacement surgery, during and following hospitalization.
• in patients undergoing knee replacement surgery.
• in medical patients who are at risk for thromboembolic complications due to severely restricted mobility during acute illness.
Treatment of Acute Deep Vein Thrombosis
Venoxtaj is indicated for:
• the inpatient treatment of acute deep vein thrombosis with or without pulmonary embolism, when administered in conjunction with warfarin sodium.
• the outpatient treatment of acute deep vein thrombosis without pulmonary embolism when administered in conjunction with warfarin sodium.
Prophylaxis of Ischemic Complications of Unstable Angina and Non-Q-Wave Myocardial Infarction
Venoxtaj is indicated for the prophylaxis of ischemic complications of unstable angina and nonQ-wave myocardial infarction, when concurrently administered with aspirin.
Treatment of Acute ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
Venoxtaj, when administered concurrently with aspirin, has been shown to reduce the rate of the combined endpoint of recurrent myocardial infarction or death in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) receiving thrombolysis and being managed medically or withpercutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Dosage And Administration
All patients should be evaluated for a bleeding disorder before administration of Venoxtaj, unless the medication is needed urgently. Since coagulation parameters are unsuitable for monitoring Venoxtaj activity, routine monitoring of coagulation parameters is not required.
For subcutaneous use, Venoxtaj should not be mixed with other injections or infusions. For intravenous use (i.e., for treatment of acute STEMI), Venoxtaj can be mixed with normal saline solution (0.9%) or 5%dextrose in water.
Venoxtaj is not intended for intramuscular administration.
Adult Dosage
Abdominal Surgery
In patients undergoing abdominal surgery who are at risk for thromboembolic complications, the recommended dose of Venoxtaj is 40 mg once a day administered by SC injection with the initial dose given 2 hours prior to surgery. The usual duration of administration is 7 to 10 days; up to 12 days administration has been administered in clinical trials.
Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery
In patients undergoing hip or knee replacement surgery, the recommended dose of Venoxtaj is 30 mg every 12 hours administered by SC injection. Provided that hemostasis has been established, the initial dose should be given 12 to 24 hours after surgery. For hip replacement surgery, a dose of 40 mg once a day SC, given initially 12 (±3) hours prior to surgery, may be considered. Following the initial phase of thromboprophylaxis in hip replacement surgery patients, it is recommended that continued prophylaxis with Venoxtaj 40 mg once a day be administered by SC injection for 3 weeks. The usual duration of administration is 7 to 10 days; up to 14 days administration has been administered in clinical trials.
Medical Patients During Acute Illness
In medical patients at risk for thromboembolic complications due to severely restricted mobility during acute illness, the recommended dose of Venoxtaj is 40 mg once a day administered by SC injection. The usual duration of administration is 6 to 11 days; up to 14 days of Venoxtaj has been administered in the controlled clinical trial.
Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis with or without Pulmonary Embolism
In outpatient treatment, patients with acute deep vein thrombosis without pulmonary embolism who can be treated at home, the recommended dose of Venoxtaj is 1 mg/kg every 12 hours administered SC. In inpatient (hospital) treatment, patients with acute deep vein thrombosis with pulmonary embolism or patients with acute deep vein thrombosis without pulmonary embolism (who are not candidates for outpatient treatment), the recommended dose of Venoxtaj is 1 mg/kg every 12 hours administered SC or 1.5 mg/kg once a day administered SC at the same time every day. In both outpatient and inpatient(hospital) treatments, warfarin sodium therapy should be initiated when appropriate (usually within 72 hours of Venoxtaj). Venoxtaj should be continued for a minimum of 5 days and until a therapeutic oral anticoagulant effect has been achieved (International Normalization Ratio 2.0 to 3.0). The average duration of administration is 7 days; up to 17 days of Venoxtaj administration has been administered in controlled clinical trials.
Unstable Angina and Non-Q-Wave Myocardial Infarction
In patients with unstable angina or non-Q-wave myocardial infarction, the recommended dose of Venoxtaj is 1 mg/kg administered SC every 12 hours in conjunction with oral aspirin therapy (100 to 325 mg once daily). Treatment with Venoxtaj should be prescribed for a minimum of 2 days and continued until clinical stabilization. The usual duration of treatment is 2 to 8 days; up to 12.5 days of Venoxtaj has been administered in clinical trials.
Treatment of Acute ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
In patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, the recommended dose of Venoxtaj is a single IV bolus of 30 mg plus a 1 mg/kg SC dose followed by 1 mg/kg administered SC every 12 hours (maximum 100 mg for the first two doses only, followed by 1 mg/kg dosing for the remaining doses). Dosage adjustments are recommended in patients ≥ 75 years of age. All patients should receive aspirin as soon as they are identified as having STEMI and maintained with 75 to 325 mg once daily unless contraindicated.
When administered in conjunction with a thrombolytic (fibrin-specific or non-fibrin specific), Venoxtaj should be given between 15 minutes before and 30 minutes after the start of fibrinolytic therapy. In the pivotal clinical study, the Venoxtaj treatment duration was 8 days or until hospital discharge, whichever came first. An optimal duration of treatment is not known, but it is likely to be longer than 8 days.
For patients managed with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI): If the last Venoxtaj SC administration was given less than 8 hours before balloon inflation, no additional dosing is needed. If the last Venoxtaj SC administration was given more than 8 hours before balloon inflation, an IV bolus of 0.3 mg/kg of Venoxtaj should be administered.
Renal Impairment
Although no dose adjustment is recommended in patients with moderate (creatinine clearance 30-50 mL/min) and mild (creatinine clearance 50-80 mL/min) renal impairment, all such patients should be observed carefully for signs and symptoms of bleeding.
Enoxaparin sodium doses in the clinical trials for prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis following abdominal or hip or knee replacement surgery or in medical patients with severely restricted mobility during acute illness ranged from 40 mg SC once daily to 30 mg SC twice daily.

